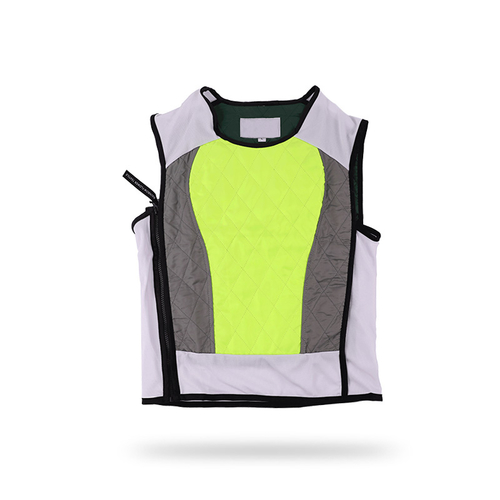
Outdoor cooling vests have become essential gear for individuals working or engaging in activities in high-temperature environments. These innovative garments employ advanced cooling technologies to help regulate body temperature, ensuring comfort and safety in challenging conditions.
Evaporative Cooling Technology:
Many outdoor cooling vests utilize evaporative cooling technology as a primary mechanism to cool the body. These vests are made from materials that have a high water absorbency, such as polymer crystals or specially designed fabrics. When these materials are soaked in water, they absorb and retain the moisture.
As the water in the vest evaporates, it absorbs heat from the body, providing a cooling effect. This process mimics the body's natural cooling mechanism through sweat evaporation. Evaporative cooling vests are effective in dry climates where the rate of evaporation is high.
Phase Change Material (PCM) Technology:
Another common technology in outdoor cooling vests involves the use of phase change materials (PCMs). PCMs are substances that undergo a phase transition (solid to liquid or vice versa) at a specific temperature. In cooling vests, these materials are often encapsulated in small packets or embedded within the fabric.
The PCMs absorb and release thermal energy as they change phases. When the temperature rises, the PCM absorbs heat, causing it to change from a solid to a liquid. This absorption of heat helps cool the body. As the temperature decreases, the PCM solidifies again, ready to repeat the cycle.
Conduction and Convection:
Some cooling vests leverage the principles of conduction and convection to dissipate heat from the body. These vests may incorporate materials that have high thermal conductivity, allowing them to absorb and transfer body heat away from the skin.
Additionally, convection plays a role as air flows over the vest, carrying away the heat absorbed by the material. This combination of conduction and convection enhances the cooling efficiency of the vest, promoting a more comfortable experience for the wearer.
Air Circulation and Ventilation:
Proper air circulation is crucial for effective cooling, and many outdoor cooling vests are designed with ventilation features. These vests may have strategically placed vents, mesh panels, or perforations that allow air to flow through, facilitating the cooling process.
The enhanced airflow helps in expelling the heat generated by the body, preventing the accumulation of heat within the vest. This is especially important in humid conditions where evaporative cooling may be less effective.
Moisture-Wicking Fabrics:
Moisture-wicking fabrics are commonly used in outdoor cooling vests to manage sweat and moisture. These fabrics draw moisture away from the skin and distribute it across a larger surface area, facilitating quicker evaporation.
By keeping the skin dry, moisture-wicking fabrics enhance the effectiveness of cooling technologies. When the skin is dry, evaporative cooling can occur more efficiently, providing a continuous cooling effect.
Adjustable Fit and Insulation:
The fit of the cooling vest also contributes to its effectiveness. Many vests are designed to be adjustable, allowing wearers to customize the fit for comfort and optimal cooling. A snug but not restrictive fit helps maximize contact between the cooling elements and the body.
Additionally, some vests incorporate insulation layers to prevent external heat from penetrating the garment. This insulation ensures that the cooling mechanisms focus on maintaining a comfortable temperature rather than combating external heat sources.
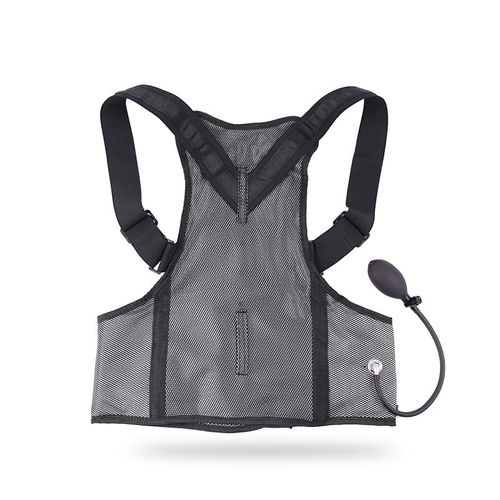
User-Controlled Activation:
To give wearers control over their cooling experience, some vests feature user-controlled activation. This may involve adjustable settings or the ability to activate cooling technologies based on individual preferences. Such control allows users to tailor the cooling effect to their specific needs and the environmental conditions.

 English
English 简体中文
简体中文







 3rd Floor, East Gate, No. 2599 Park Road, Sheng Ze Town, Wu Jiang District, Suzhou City, Jiangsu Province
3rd Floor, East Gate, No. 2599 Park Road, Sheng Ze Town, Wu Jiang District, Suzhou City, Jiangsu Province  +86- 0512-63519080
+86- 0512-63519080
 +86-13584404311
+86-13584404311  FQsales1@163.com
FQsales1@163.com